Cruzamiento exitoso de Arachis duranensis como madre con A. ipaёnsis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.30972/bon.3316981Palabras clave:
Donante de genoma A, donante de genoma B, híbrido, origen del maní cultivadoResumen
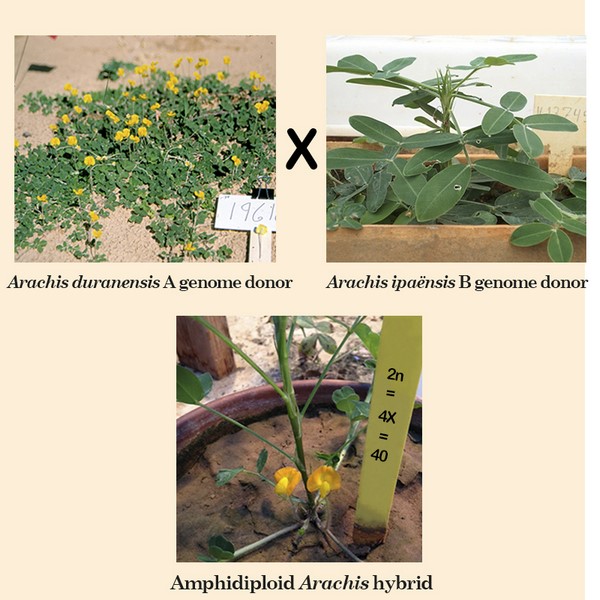
Arachis hypogaea L. se originó en América del Sur y ha sido llevado a gran parte de las zonas tropicales y subtropicales del mundo como un valioso cultivo alimenticio con alto contenido de proteínas y como una fuente de aceite insaturado. El origen del maní cultivado, 2n = 4x = 40, ha sido objeto de muchas discusiones, pero la mayoría concuerda en que A. duranensis sería el donante del genoma A y A. ipaënsis el donante B; ambos diploides con 2n = 20. También es objeto de debate si la duplicación cromosómica de este híbrido ocurrió en un entorno natural o en el jardín de un cazador-recolector-cultivador. Los análisis moleculares han establecido que A. duranensis fue el progenitor femenino del cruzamiento. Hasta hace poco nadie había tenido éxito en hacer el cruzamiento y establecer plantas del mismo en esa dirección. El cruzamiento recíproco se logra fácilmente y se ha informado varias veces. El objetivo principal de este trabajo es informar sobre el éxito del cruzamiento y el desarrollo de plantas híbridas, anfidiploides y poblaciones del híbrido A. duranensis × A. ipaënsis.
Descargas
Citas
Banks, D. J. (1977). A colchicine method which achieves fertility in interspecific peanut hybrids. Proceedings American Peanut Research and Education Association 9: 30 (Abst.).
Bertioli, D. J., Cannon, S. B., Froenicke, L., Huang, G., Farmer, A. D., Cannon, E. K. S., Liu, X., Gao, D., Clevenger, J., Dash, S., Ren, K., Moretzsohn, M. C., Shirasawa, K., Huang, W., Vidigal, B., Abernathey, B., Chu, Y., Niederhuth, C. E., Umale, P., Araújo, A. C. G., Kozik, A., Kim, K. D., Burow, M. D., Varshney, R. K., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Barkley, N., Guimarães, P. M., Guo, B., Liao, B., Stalker, H. T., Schmitz, R. J., Scheffler, B. E., Leal-Bertioli, S. C. M., Xun, X., Jackson, S. A., Michelmore, R. & Ozias-Akins, P. (2016a). The genome sequences of Arachis duranensis and Arachis ipaënsis, the diploid ancestors of cultivated peanut. Nature 48: 438-446. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3517
Bertioli, D. J., Leal-Bertioli, S. C. M. & Stalker, H. T. (2016b). The Peanut Genome: The History of the Consortium and the structure of the genome of cultivated peanut and its diploid ancestors. In Stalker, H. T. & R. F. Wilson (eds.), Peanuts: Genetics, Processing and Utilization, pp. 147-161. Academic Press and AOCS Press, Waltham, MA. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-63067-038-2.00005-8
Burow, M. D., Simpson, C. E., Starr, J. L. & Patterson, A. H. (2001). Transmission genetics of chromatin from a synthetic amphidiploid to cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Broadening the gene pool of a monophyletic polyploid species. Genetics 154: 823-837. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/159.2.823
Custodio, A. R., Peñaloza, A. P. S. & Valls, J. F. M. (2005). Further cytogenetic information on Arachis stenosperma (Leguminosae). Cytologia 70: 331-335.
https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.70.331
D’Cruz, R. & Chakravarty, K. (1961). Spontaneous alloploidy in Arachis. Indian Oil Seeds J. 5: 55-57.
Fávero, A. P., Simpson, C. E., Valls, J. F. M. & Velo, N. A. (2006). Study of evolution of cultivated peanut through crossability studies among Arachis ipaënsis, A. duranensis and A. hypogaea. Crop Science 46: 1546-1552. htps://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2005.09-0331
García, A. V., Ortiz, A. M., Silvestri, M. C., Custodio, A. R., Moretzsohn, M. C., & Lavia, G. I. (2020). Occurrence of 2n microspore production in diploid interspecific hybrids between the wild parental species of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L., Leguminosae) and its relevance in the genetic origin of the cultigen. Crop Science 60: 2420-2436. htps://doi:10.1002/csc2.2020233
Grabiele, M., Chalup, L., Robledo, R. & Seijo, J. G. (2012). Genetic and geographic origin of domesticated peanut as evidenced by 5S rDNA and chloroplast DNA sequences. Plant Systematics and Evolution 298: 1151-1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-12-0627-3
Gregory, M. P. & Gregory, W. C. (1979). Exotic germplasm of Arachis L. interspecific hybrids. Journal of Heredity. 70: 185-193. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a109231
Gregory, W. C., Krapovickas, A. & Gregory, M. P. (1980). Structures, variation, evolution and classification in Arachis. In Summerfield, R. J. & A. H. Bunting (eds.), Advances in Legume Science, pp. 469-481. Royal Botanic Gardens, London.
Husted, L. (1936). Cytological studies on the peanut Arachis. II Chromosome number, morphology and behavior, and their application to the problem of origin of the cultivated forms. Cytologia 7: 396-423. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.7.396
Kochert, G., Halward, T., Branch, W. D. & Simpson, C. E. (1991). RFLP variability in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars and wild species. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 81: 565-570. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226719
Kochert, G., Stalker, H. T., Gimenes, M., Galgaro, L., Lopes, C. R. & Moore, K. (1996). RFLP and cytogenetic evidence on the origin and evolution of allotetraploid domesticated peanut, Arachis hypogaea (Leguminosae). American Journal of Botany 83:1282-1291. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1996.tb13912.x
Krapovickas, A. (1969). The origin, variability and spread of the groundnut (Arachis hypogaea). In Ucko, P. J. & G. W. Dimbleby (eds.), The domestication and exploitation of plants and animals, pp. 427-441. Duckworth, London. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315131825-39
Krapovickas, A. & Gregory, W. C. (1994). Taxonomía del género Arachis. (Leguminosae). Bonplandia 8: 1-186.
Krapovickas, A. & Gregory, W. C. (2007). Taxonomy of the genus Arachis (Leguminosae). Translated by D. E. Williams and C. E. Simpson. Bonplandia 16 (Supl.): 1-205. https://doi.org/10.30972/bon.160158
Kumar, L. S. S., D’Cruz, R. & Oke, J. G. (1957). A Synthetic allohexaploid in Arachis. Current Science 26: 121-122.
Lu, J. & Pickersgill, B. (1993). Isozyme variation and species relationships in peanut and its wild relatives (Arachis L. – Leguminosae). Theoretical and Applied Genetics 85: 550-560. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220913
Robledo. G., Lavia, G. I. & Seijo, J. G. (2009). Species relationships among wild Arachis species with the A genome revealed by FISH mapping of rDNA loci and heterochromatin detection. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 118: 1295-1307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-0981-x
Robledo, G. & Seijo, J. G. (2010). Species relationships among the wild B genome of Arachis species (section Arachis) based on FISH mapping of rDNA loci and heterochromatin detection: a new proposal for genome arrangement. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 121: 1033-1046. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1369-7
Seijo, J. G., Lavia, G. I., Fernández, A., Krapovickas, A., Ducasse, D. & Moscone, E. A. (2004). Physical mapping of the 5S and 18S-25S rRNA genes by FISH as evidence that Arachis duranensis and A. ipaënsis are the wild diploid progenitors of A. hypogaea (Leguminosae). American Journal of Botany 91: 1294-1303. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.91.9.1294
Seijo, J. G., Lavia, G. I., Fernández, A., Krapovickas, A., Ducasse, D., Bertioli, D. A. & Moscone, E. A. (2007). Genomic relationships between the cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea, Leguminosae) and its close relatives revealed by double GISH. American Journal of Botany 94: 1963-1971. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.94.12.1963
Seijo, J. G., Atahuachi, M., Simpson, C. E. & Krapovickas, A. (2021). Arachis inflata: A new B genome species of Arachis (Fabaceae). Bonplandia 30: 169-174. https://doi.org/10.30972/bon.3024942
Singh, A. K. (1988). Putative genome donors of Arachis hypogaea (Fabaceae). Evidence from crosses with synthetic amphidiploids. Plant Systematics and Evolution. 160: 143-151. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936041
Singh, A. K. & Smartt, J. (1998). The genome donors of the groundnut/peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) revisited. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 45: 113-118.
Simpson, C. E. & Davis, K. S. (1983). Meiotic behavior of a male-fertile triploid Arachis L. hybrid. Crop Science 23: 581-584. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1983.0011183X002300030032x
Simpson, C. E. (1991). Pathways for introgression of pest resistance into Arachis hypogaea L. Peanut Science 18: 22-26. https://doi.org/10.3146/i0095-3679-18-1-8
Simpson, C. E., Krapovickas, A. & Valls, J. F. M. (2001). History of Arachis including evidence of A. hypogaea L. progenitors. Peanut Science 28: 78-80.
https://doi.org/10.3146/i0095-3679-28-2-7
Simpson, C. E. (2017). Finally, the cross that made Arachis monticola Krapov. & Rigoni and/or Arachis hypogaea L. Proceedings of The American Peanut Research and Education Society 49: 66.
Smartt, J., Gregory, W. C. & Gregory, M. P. (1978). The Genomes of Arachis hypogaea. I. Cytogenetic studies of putative genome donors. Euphytica 27: 665675. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023701
Valls, J. F. M. & Simpson, C. E. (2005). New species of Arachis (Leguminosae) from Brazil, Paraguay and Bolivia. Bonplandia 14: 35-63. https://doi.org/10.30972/bon.141-21387
Valls, J. F. M., Costa, L. C. & Custodio, A. R. (2013). A novel trifoliolate species of Arachis (Fabaceae) and further comments on the taxonomic section Trierectoides. Bonplandia 22: 91-97. https://doi.org/10.30972/bon.2211257
Valls, J. F. M. & Simpson, C. E. (2017). A new species of Arachis (Fabaceae) from Mato Grosso, Brazil related to Arachis matiensis. Bonplandia 26: 143-149. https://doi.org/10.30972/bon.2622575
Descargas
Publicado
Versiones
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2023 Bonplandia

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Declaration of Adhesion to Open Access
- All contents of Bonplandia journal are available online, open to all and for free, before they are printed.
Copyright Notice
- Bonplandia magazine allows authors to retain their copyright without restrictions.
- The journal is under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.














.jpg)


